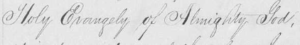Occasionally, we each run into difficulty interpreting handwriting in old documents. It comes with the territory. Modern genealogists are not the only ones affected by the problem. Decades ago, clerks who hand copied original documents ran into the same issue. Worse, publishers then printed typeset versions of those recopied texts (or abstracts of them). Once a misinterpreted word gets into print, it becomes accepted wisdom and resistant to change.
The situation is particularly vexing when the misinterpreted word is a person’s name. Willis and Willey provide a good example. Families of each surname lived close to each other in early Dorchester County, Maryland. The handwritten name Willis in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries often ended with a downward swooping tail on the “s,” which made it look like a “y.” [1]
The following illustrates the script anomaly. Parties to legal documents of the era often took an oath on the “Holy Evangels of Almighty God,” meaning the Christian Gospels. Here is the way that phrase appears in a Dorchester County Will Book:
There is no discernable difference in the “y” at the end of the words Holy and Almighty and what is supposed to be an “s” at the end of Evangels. The scribe who recopied this deed into a nicely readable volume misread a long-tailed “s” in the original, writing it as a “y.”
No harm done. We know there is no such word as “Evangely,” so we can just move on … maybe tsk, tsk-ing under our breath. But what of the poor Willis and Willey families? A similar misread could easily convert a Willis into a Willey, or vice versa. In fact, an authoritative source of marriages in early Maryland states that Francis Insley married Keziah Willey on 27 Oct 1785 in Dorchester County.[2] However, a land sale by that couple twenty years later provides evidence that the bride’s name was actually Keziah Willis, not Willey.
In 1805, the Insleys’s sold 60 acres of land called “Addition to Adventure.”[3] The Willis family had owned that parcel for four decades, dating back to Richard Willis’s purchase in 1764.[4] The 1805 Insley deed recites that Benedict Meekins and his wife Mary [nee Willis] had sold the land to Andrew Willis, who devised it to his son Andrew. The deed does not state how Francis Insley and his wife Keziah got title to the land from the younger Andrew, and there are no other deeds that explain their ownership.
Explaining the Insley’s ownership is simple, however, if Keziah’s maiden name were Willis rather than Willey. Keziah was one of four children of the elder Andrew Willis and his wife Sarah.[5] The elder Andrew willed the land to his son Andrew, Jr. The younger Andrew subsequently died without a will and without children some time after 1796. His estate therefore passed to his heirs as defined under the Maryland laws of intestate descent and distribution, i.e., his siblings and the children of any already deceased siblings.
Keziah Willis Insley and her husband possessed the land in 1805 because she was Andrew’s only surviving sibling, and her brother George and sister Mary had each died without surviving children. Dorchester records make no mention in the relevant time frame of either George or Mary — no marriage, deed, death, or migration information. Their absence from the record supports the theory that they both died young and without issue.
The circumstantial evidence is sufficient to conclude that 1) a transcriber erroneously interpreted Keziah’s last name in the marriage record, 2) that Francis Insley married Keziah Willis in 1785, and 3) she was a party to the sale of Willis family land twenty years later.
The critical misinterpretation of Keziah Willis’s name will never be corrected in most published sources, but some of us will know the truth.
[1]Lower case “i” and “e” are also hard to distinguish.
[2]Palmer, Katherine H., Dorchester County, Maryland: Marriage License Records, 1780-1855, 1960.
[3]McAllister, James A., Jr., Abstracts from the Land Records of Dorchester County, Maryland, Volume 42 (Liber HD No. 21), Cambridge, Maryland, 21 HD 569
[4]McAllister, Abstracts, Volume 15 (Liber Old No. 19), Cambridge, Maryland, 1964, 19 Old 163
[5]Old Trinity Church records show that the elder Andrew Willis and his wife Sarah baptized three children — Andrew, Keziah, and George — between 1768 and 1775. The couple also had a fourth child, Mary.